Regardless of the content to be displayed and the application scene, various image systems need some way to control the viewer's viewing effect.
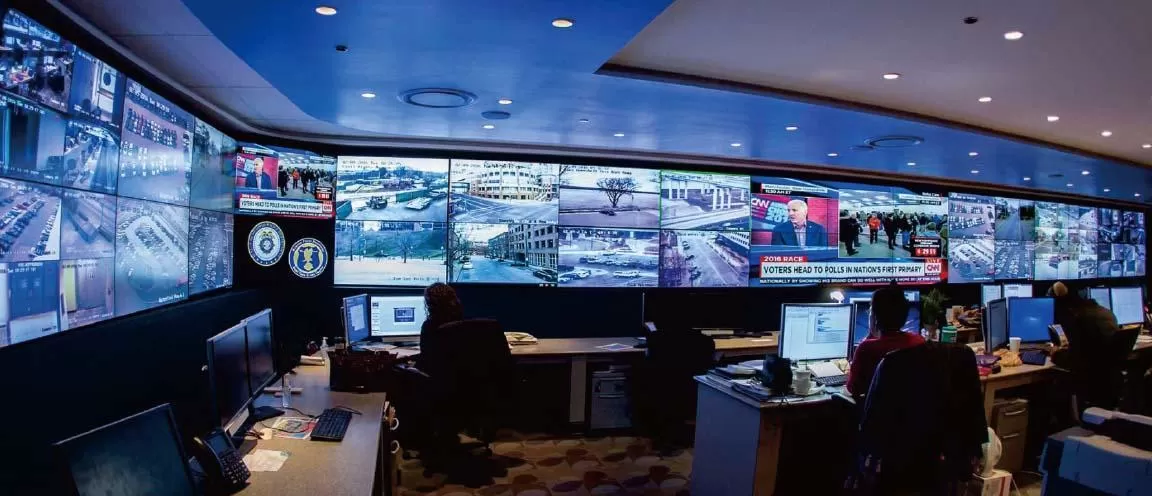
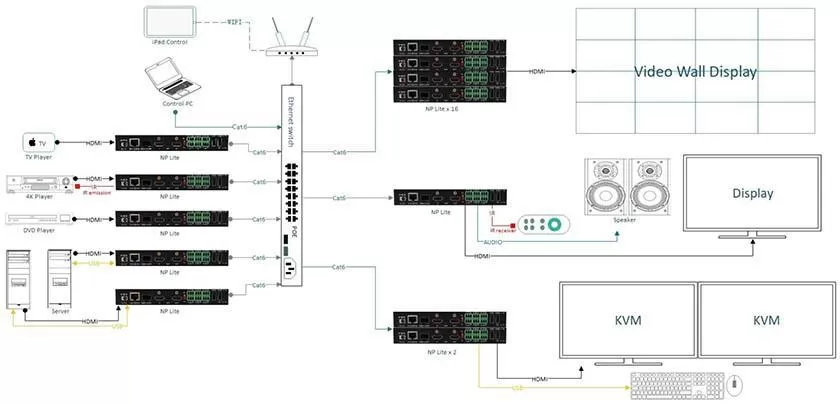
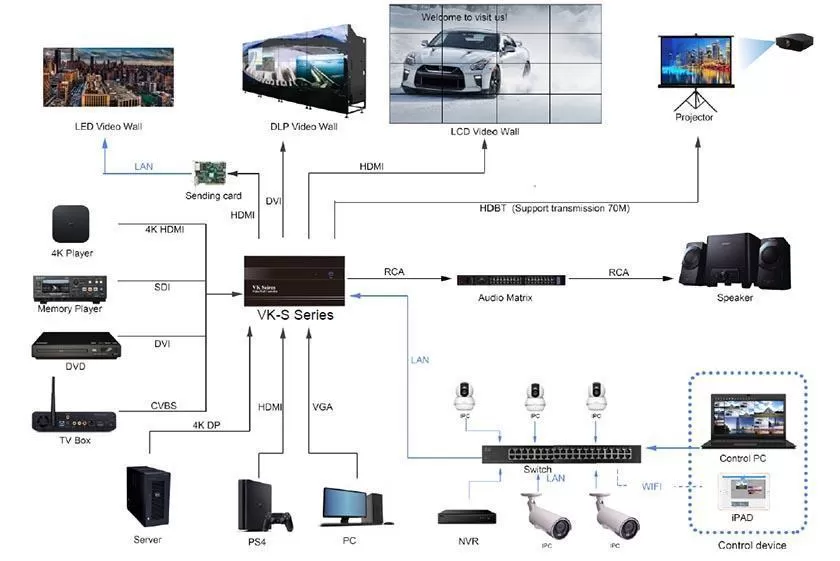
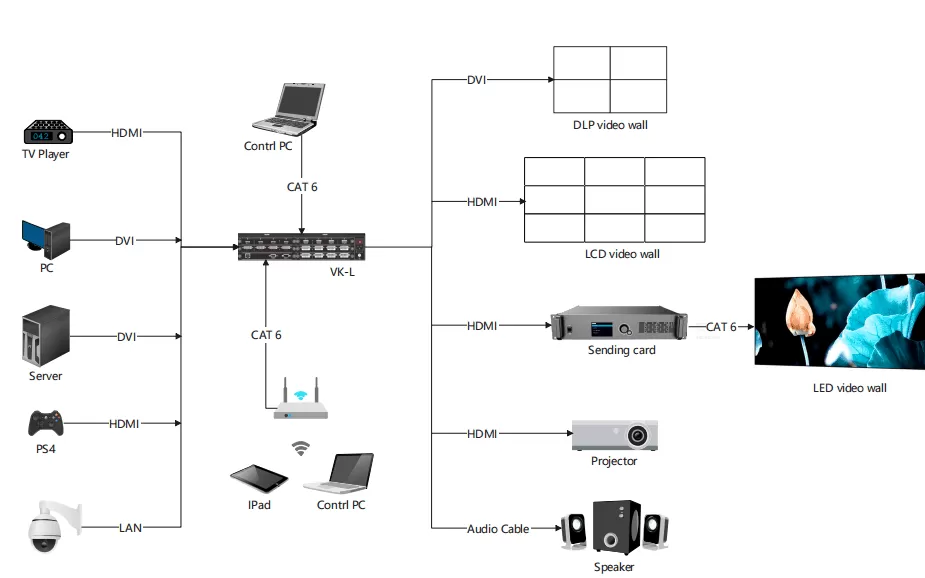
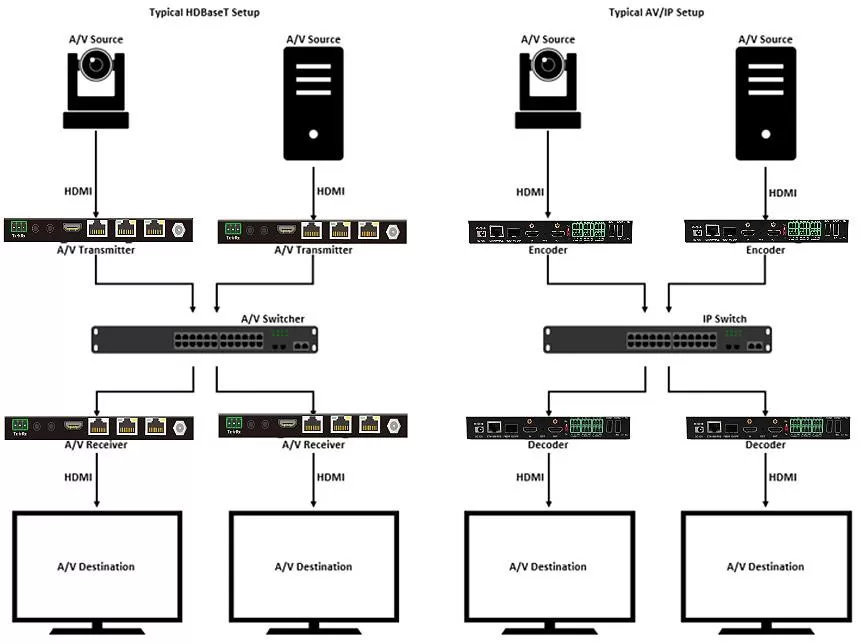
At present, the mainstream LCD splicing video wall can form a link between the screen and the screen through LOOP, thereby displaying a complete image, but if you need to display multiple video resources on the video wall at the same time in your application Move the position of all display windows freely, then you need a video processor to build a complete video wall control system. Imagine, a control room or a monitoring room-the more advanced and complex the system, the more powerful control mechanisms are necessary. However, not every controller system is the same. The best system provides the greatest flexibility and provides the necessary tools for the audiovisual personnel of enterprises or government organizations. Of course.
Now the controller has more functions waiting for your experience, such as: Scrolling Text (generate a piece of text that can be moved anywhere on the video wall), signal clip (cut any content in the signal source window to display), etc. The controller also supports a variety of signal source interfaces, HDMI / DVI / SDI / CVBS / DP..., even the IP stream of the network can be seamlessly accessed. No matter what type of your signal source equipment is, you can display them on the video wall through the video processor.
These features will help you get a better visual experience and receive more information.